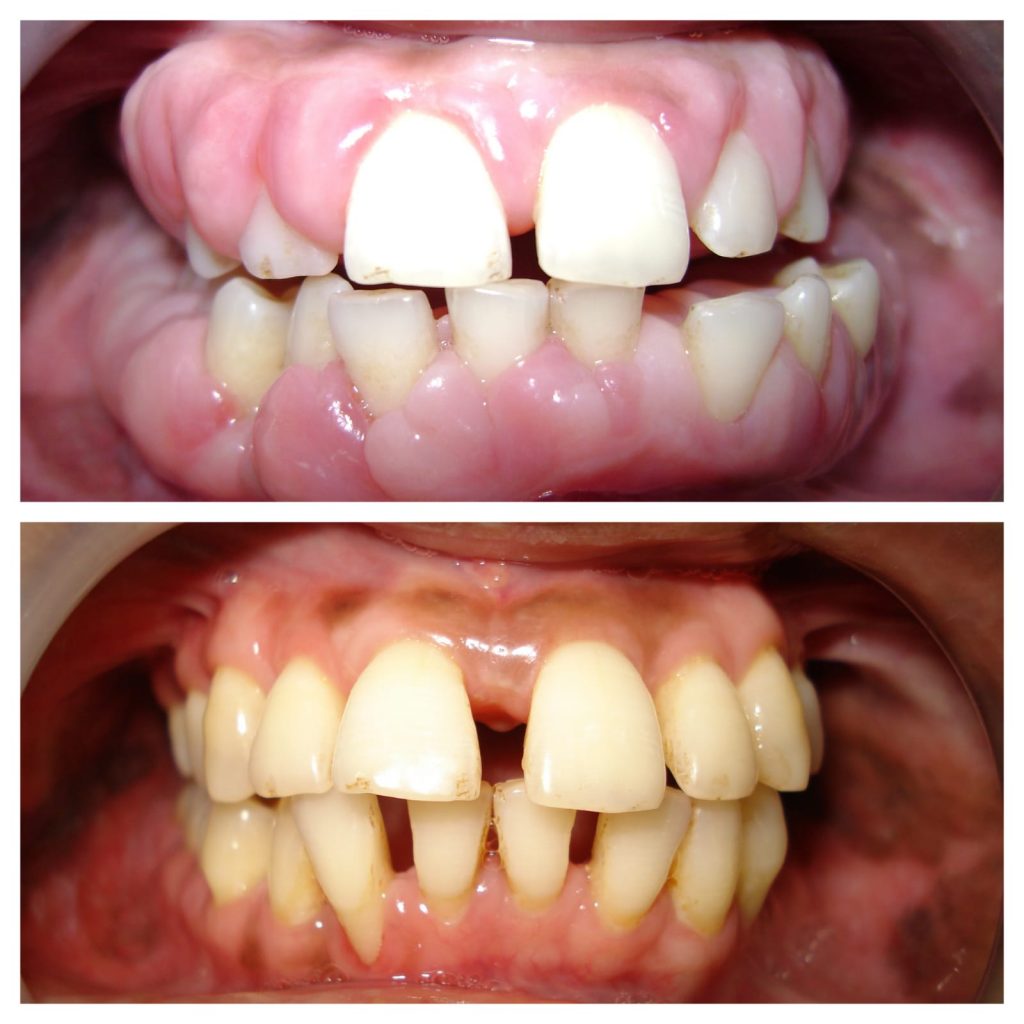
Advanced Gum Surgeries
Gum diseases such as gingivitis and periodontitis may require surgical treatment. Gingivitis is a mild form that causes redness, swelling, and bleeding, mostly due to poor oral hygiene, plaque, and tartar buildup. Professional treatment can reverse this condition.
Periodontitis is a severe gum disease where inflammation destroys bone and tissues. Gums begin to separate from teeth, forming pockets that trap infection. This leads to bone loss and potential tooth loss.
When non-invasive treatments fail, the dentist may recommend one of these surgical procedures:
• Pocket Reduction Surgery (Flap Surgery)
Small incisions are made to fold gums back and access deep plaque. Bacteria are removed, roots cleaned, and gums stitched back to reduce pocket depth.
• Soft Tissue Grafts
If gum recession has caused tissue loss, a graft from the roof of the mouth restores healthy gum structure, protects teeth, and improves appearance.
• Bone Grafts
Severe bone loss may require grafting. Small pieces of bone with growth factors are placed to stimulate natural bone regeneration.
After surgery, maintaining gum health is essential. Routine brushing, flossing, mouthwash, and professional cleanings help prevent disease recurrence.


